 |
 |
 |
|
|
 LATEST NEWS LATEST NEWS
 Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh dolor sit elit, sed diam nonummy nibh commodo consequat. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh dolor sit elit, sed diam nonummy nibh commodo consequat.
Read more
 Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh dolor sit elit, sed diam nonummy nibh commodo consequat. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh dolor sit elit, sed diam nonummy nibh commodo consequat.
Read more
 Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh dolor sit elit, sed diam nonummy nibh commodo consequat. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh dolor sit elit, sed diam nonummy nibh commodo consequat.
Read more
|

|
|
TAXI SERVICE HENG, ABOUT - CAMBODIA
|
Background:
|


Most Cambodians consider themselves to be Khmers, descendants of the Angkor
Empire that extended over much of Southeast Asia and reached its zenith
between the 10th and 13th centuries. Attacks by the Thai and Cham (from
present-day Vietnam) weakened the empire ushering in a long period of
decline. The king placed the country under French protection in 1863.
Cambodia became part of French Indochina in 1887. Following Japanese
occupation in World War II, Cambodia gained full independence from France in
1953. In April 1975, after a five-year struggle, Communist Khmer Rouge
forces captured Phnom Penh and evacuated all cities and towns. At least 1.5
million Cambodians died from execution, forced hardships, or starvation
during the Khmer Rouge regime under POL POT. A December 1978 Vietnamese
invasion drove the Khmer Rouge into the countryside, began a 10-year
Vietnamese occupation, and touched off almost 13 years of civil war. The
1991 Paris Peace Accords mandated democratic elections and a ceasefire,
which was not fully respected by the Khmer Rouge. UN-sponsored elections in
1993 helped restore some semblance of normalcy under a coalition government.
Factional fighting in 1997 ended the first coalition government, but a
second round of national elections in 1998 led to the formation of another
coalition government and renewed political stability. The remaining elements
of the Khmer Rouge surrendered in early 1999. Some of the remaining Khmer
Rouge leaders are awaiting trial by a UN-sponsored tribunal for crimes
against humanity. Elections in July 2003 were relatively peaceful, but it
took one year of negotiations between contending political parties before a
coalition government was formed. |
|
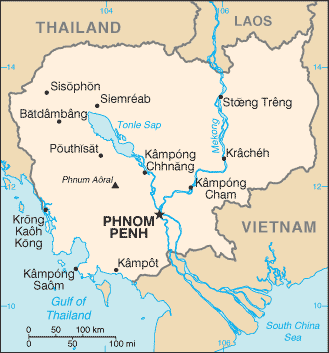
Location:
|


Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, between Thailand,
Vietnam, and Laos |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|


13 00 N, 105 00 E |
|
Map references:
|


Southeast Asia |
|
Area:
|



total: 181,040 sq km
land: 176,520 sq km
water: 4,520 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|


slightly smaller than Oklahoma |
|
Land boundaries:
|


total: 2,572 km
border countries: Laos 541 km, Thailand 803 km, Vietnam 1,228 km
|
|
Coastline:
|


443 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|


territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm |
|
Climate:
|


tropical; rainy, monsoon season (May to November); dry season (December to
April); little seasonal temperature variation |
|
Terrain:
|


mostly low, flat plains; mountains in southwest and north |
|
Elevation extremes:
|


lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m
highest point: Phnum Aoral 1,810 m |
|
Natural resources:
|


oil and gas, timber, gemstones, some iron ore, manganese, phosphates,
hydropower potential |
|
Land use:
|


arable land: 20.44%
permanent crops: 0.59%
other: 78.97% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|


2,700 sq km (2003) |
|
Natural hazards:
|


monsoonal rains (June to November); flooding; occasional droughts
|
|
Environment - current issues:
|


illegal logging activities throughout the country and strip mining for gems
in the western region along the border with Thailand have resulted in
habitat loss and declining biodiversity (in particular, destruction of
mangrove swamps threatens natural fisheries); soil erosion; in rural areas,
most of the population does not have access to potable water; declining fish
stocks because of illegal fishing and overfishing |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|


party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto
Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life
Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 94,
Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea |
|
Geography - note:
|


a land of paddies and forests dominated by the Mekong River and Tonle Sap
|
|
Population:
|



13,995,904
note: estimates for this country take into account the effects of
excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy,
higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population growth rates, and
changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would
otherwise be expected (July 2007 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|


0-14 years: 34% (male 2,405,561/female 2,355,404)
15-64 years: 62.4% (male 4,234,701/female 4,500,994)
65 years and over: 3.6% (male 189,090/female 310,154) (2007 est.)
|
|
Median age:
|


total: 21.3 years
male: 20.6 years
female: 22.1 years (2007 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|


1.729% (2007 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|



25.53 births/1,000 population (2007 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|



8.24 deaths/1,000 population (2007 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|


0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2007 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|


at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.021 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.941 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.61 male(s)/female
total population: 0.953 male(s)/female (2007 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|



total: 58.45 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 65.74 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 50.84 deaths/1,000 live births (2007 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|



total population: 61.29 years
male: 59.27 years
female: 63.4 years (2007 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|



3.12 children born/woman (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|



2.6% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|



170,000 (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|



15,000 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|


degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea,
hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, and Japanese
encephalitis are high risks in some locations
note: highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified
among birds in this country or surrounding region; it poses a negligible
risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close
contact with birds (2007) |
|
Nationality:
|


noun: Cambodian(s)
adjective: Cambodian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|


Khmer 90%, Vietnamese 5%, Chinese 1%, other 4% |
|
Religions:
|


Theravada Buddhist 95%, other 5% |
|
Languages:
|


Khmer (official) 95%, French, English |
|
Literacy:
|


definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 73.6%
male: 84.7%
female: 64.1% (2004 est.) |
|
Country name:
|


conventional long form: Kingdom of Cambodia
conventional short form: Cambodia
local long form: Preahreacheanachakr Kampuchea (phonetic
pronunciation)
local short form: Kampuchea
former: Khmer Republic, Democratic Kampuchea, People's Republic of
Kampuchea, State of Cambodia |
|
Government type:
|


multiparty democracy under a constitutional monarchy |
|
Capital:
|


name: Phnom Penh
geographic coordinates: 11 33 N, 104 55 E
time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC during
Standard Time) |
|
Administrative divisions:
|


20 provinces (khaitt, singular and plural) and 4 municipalities* (krong,
singular and plural)
provinces: Banteay Mean Cheay, Batdambang, Kampong Cham, Kampong
Chhnang, Kampong Spoe, Kampong Thum, Kampot, Kandal, Kaoh Kong, Krachen,
Mondol Kiri, Otdar Mean Cheay, Pouthisat, Preah Vihear, Prey Veng, Rotanah
Kiri, Siem Reab, Stoeng Treng, Svay Rieng, Takev
municipalities: Keb, Pailin, Phnum Penh (Phnom Penh), Preah Seihanu
(Sihanoukville) |
|
Independence:
|


9 November 1953 (from France) |
|
National holiday:
|


Independence Day, 9 November (1953) |
|
Constitution:
|


promulgated 21 September 1993 |
|
Legal system:
|


primarily a civil law mixture of French-influenced codes from the United
Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) period, royal decrees,
and acts of the legislature, with influences of customary law and remnants
of communist legal theory; increasing influence of common law; accepts
compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations |
|
Suffrage:
|


18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|


chief of state: King Norodom SIHAMONI (since 29 October 2004)
head of government: Prime Minister HUN SEN (since 14 January 1985);
Deputy Prime Ministers SAR KHENG (since 3 February 1992); SOK AN, LU LAY
SRENG, TEA BANH, HOR NAMHONG, NHEK BUNCHHAY (since 16 July 2004); KEV PUT
REAKSMEI (since 24 October 2006), BIN CHHIN (since 5 September 2007)
cabinet: Council of Ministers in theory appointed by the monarch; in
practice named by the prime minister
elections: none; the monarch is chosen by a Royal Throne Council;
following legislative elections, a member of the majority party or majority
coalition is named prime minister by the Chairman of the National Assembly
and appointed by the king |
|
Legislative branch:
|


bicameral, consists of the National Assembly (123 seats; members elected by
popular vote to serve five-year terms) and the Senate (61 seats; 2 members
appointed by the monarch, 2 elected by the National Assembly, and 57 elected
by parliamentarians and commune councils; members serve five-year terms)
elections: National Assembly - last held 27 July 2003 (next to be
held in July 2008); Senate - last held 22 January 2006 (next to be held in
January 2011)
election results: National Assembly - percent of vote by party - CPP
47%, SRP 22%, FUNCINPEC 21%, other 10%; seats by party - CPP 73, FUNCINPEC
26, SRP 24; Senate - percent of vote by party - CPP 69%, FUNCINPEC 21%, SRP
10%; seats by party - CPP 45, FUNCINPEC 10, SRP 2 (January 2006)
|
|
Judicial branch:
|


Supreme Council of the Magistracy (provided for in the constitution and
formed in December 1997); Supreme Court (and lower courts) exercises
judicial authority |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|


Cambodian People's Party or CPP [CHEA SIM]; National United Front for an
Independent, Neutral, Peaceful, and Cooperative Cambodia or FUNCINPEC [KEV
PUT REAKSMEI]; Norodom Ranariddh Party or NRP [Norodom RANARIDDH]; Sam
Rangsi Party or SRP [SAM RANGSI] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|


NA |
|
International organization participation:
|


ACCT, APT, ARF, AsDB, ASEAN, EAS, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA,
IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (subscriber),
ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIS, UNWTO,
UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|


chief of mission: Ambassador EK SEREYWATH
chancery: 4530 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
telephone: [1] (202) 726-7742
FAX: [1] (202) 726-8381 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|


chief of mission: Ambassador Joseph A. MUSSOMELI
embassy: #1, Street 96, Sangkat Wat Phnom, Khan Daun Penh, Phnom Penh
mailing address: Box P, APO AP 96546
telephone: [855] (23) 728-000
FAX: [855] (23) 728-600 |
|
Flag description:
|


three horizontal bands of blue (top), red (double width), and blue with a
white three-towered temple representing Angkor Wat outlined in black in the
center of the red band; only national flag to incorporate an actual building
in its design |
|
Economy - overview:
|


In 1999, the first full year of peace in 30 years, the government made
progress on economic reforms. The US and Cambodia signed a Bilateral Textile
Agreement, which gave Cambodia a guaranteed quota of US textile imports and
established a bonus for improving working conditions and enforcing Cambodian
labor laws and international labor standards in the industry. From 2001 to
2004, the economy grew at an average rate of 6.4%, driven largely by an
expansion in the garment sector and tourism. With the January 2005
expiration of a WTO Agreement on Textiles and Clothing, Cambodia-based
textile producers were forced to compete directly with lower-priced
producing countries such as China and India. Better-than-expected garment
sector performance led to more than 13% growth in 2006. Faced with the
possibility that its vibrant garment industry, with more than 200,000 jobs,
could be in serious danger, the Cambodian government has committed itself to
a policy of continued support for high labor standards in an attempt to
maintain favor with buyers. The tourism industry continues to grow rapidly,
with foreign visitors surpassing 1 million per year beginning in 2005. In
2005, exploitable oil and natural gas deposits were found beneath Cambodia's
territorial waters, representing a new revenue stream for the government
once commercial extraction begins in the coming years. Mining also is
attracting significant investor interest, particularly in the northeastern
parts of the country. The long-term development of the economy remains a
daunting challenge. The Cambodian government is working with bilateral and
multilateral donors, including the World Bank and IMF, to address the
country's many pressing needs. The major economic challenge for Cambodia
over the next decade will be fashioning an economic environment in which the
private sector can create enough jobs to handle Cambodia's demographic
imbalance. More than 50% of the population is less than 21 years old. The
population lacks education and productive skills, particularly in the
poverty-ridden countryside, which suffers from an almost total lack of basic
infrastructure. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|



$38.89 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|


$6.6 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|



10.5% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|



$2,800 (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|


agriculture: 35.1%
industry: 26.2%
services: 38.6% (2006 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|



7 million (2003 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|


agriculture: 75%
industry: NA%
services: NA% (2004 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|



2.5% (2000 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|


35% (2004) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage
share:
|


lowest 10%: 2.9%
highest 10%: 34.8% (2004) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|


41.7 (2004 est.) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|



4.7% (2006 est.) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|



19.3% of GDP (2006 est.) |
|
Budget:
|


revenues: $836.2 million
expenditures: $978.7 million; including capital expenditures of $291
million (2006 est.) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|


rice, rubber, corn, vegetables, cashews, tapioca |
|
Industries:
|


tourism, garments, rice milling, fishing, wood and wood products, rubber,
cement, gem mining, textiles |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|



22% (2002 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|



134 million kWh (2005) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|



206.6 million kWh (2005) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|


0 kWh (2005) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|


82 million kWh (2005) |
|
Oil - production:
|



0 bbl/day (2004) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|



3,750 bbl/day (2004 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|



NA bbl/day |
|
Oil - imports:
|



NA bbl/day |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|



0 bbl |
|
Natural gas - production:
|



0 cu m (2005 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|



0 cu m (2005 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|



-$337.3 million (2006 est.) |
|
Exports:
|



$3.693 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|


clothing, timber, rubber, rice, fish, tobacco, footwear |
|
Exports - partners:
|


US 53.3%, Hong Kong 15.2%, Germany 6.6%, UK 4.3% (2006) |
|
Imports:
|



$4.749 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|


petroleum products, cigarettes, gold, construction materials, machinery,
motor vehicles, pharmaceutical products |
|
Imports - partners:
|


Hong Kong 18.1%, China 17.5%, Thailand 13.9%, Taiwan 12.7%, Vietnam 9%,
Singapore 5.3%, South Korea 4.9%, Japan 4.3% (2006) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|


$537.8 million pledged in grants and concession loans for 2005 by
international donors |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|



$1.411 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|



$3.636 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|


$NA |
|
Currency (code):
|


riel (KHR) |
|
Exchange rates:
|


riels per US dollar - 4,103 (2006), 4,092.5 (2005), 4,016.25 (2004),
3,973.33 (2003), 3,912.08 (2002) |
|
Fiscal year:
|


calendar year |
|
Airports:
|



17 (2007) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|


total: 6
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2007) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|


total: 11
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 9
under 914 m: 1 (2007) |
|
Heliports:
|


1 (2007) |
|
Railways:
|



total: 602 km
narrow gauge: 602 km 1.000-m gauge (2006) |
|
Roadways:
|



total: 38,257 km
paved: 2,406 km
unpaved: 35,851 km (2004) |
|
Waterways:
|



2,400 km (mainly on Mekong River) (2005) |
|
Merchant marine:
|



total: 586 ships (1000 GRT or over) 1,889,909 GRT/2,682,881 DWT
by type: bulk carrier 40, cargo 487, chemical tanker 10, container 9,
livestock carrier 3, passenger/cargo 5, petroleum tanker 11, refrigerated
cargo 18, roll on/roll off 1, specialized tanker 1, vehicle carrier 1
foreign-owned: 463 (Canada 6, China 166, Cyprus 9, Egypt 14, Estonia
1, Gabon 1, Greece 5, Hong Kong 11, Indonesia 1, Japan 3, South Korea 29,
Latvia 2, Lebanon 7, Nigeria 2, Romania 1, Russia 112, Singapore 2, Syria
32, Taiwan 1, Turkey 20, Ukraine 27, UAE 2, US 6, Yemen 3) (2007)
|
|
Ports and terminals:
|


Phnom Penh, Preah Seihanu (Sihanoukville) |
|
Military branches:
|


Royal Cambodian Armed Forces: Royal Cambodian Army, Royal Khmer Navy, Royal
Cambodian Air Force (2005) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|


conscription law of October 2006 requires all males between 18-30 to
register for military service; 18-month service obligation (2006)
|
|
Manpower available for military service:
|


males age 18-49: 3,002,718
females age 18-49: 3,108,254 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|


males age 18-49: 1,955,141
females age 18-49: 2,048,611 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching military service age
annually:
|


males age 18-49: 175,497
females age 18-49: 172,788 (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|



3% (2005 est.) |
|
Disputes - international:
|


Southeast Asian states must maintain border surveillance to check the spread
of avian flu; Cambodia and Thailand dispute sections of boundary with
missing boundary markers and claims of Thai encroachments into Cambodian
territory; maritime boundary with Vietnam is hampered by unresolved dispute
over sovereignty of offshore islands; Cambodia accuses Thailand of
obstructing access to Preah Vihear temple ruins awarded to Cambodia by ICJ
decision in 1962 |
|
Trafficking in persons:
|


current situation: Cambodia is a source, destination, and transit
country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of sexual
exploitation and forced labor; a significant number of women and children
are trafficked to Thailand and Malaysia for commercial sexual exploitation
and forced labor; men are trafficked primarily to Thailand for forced labor
in the construction and agricultural sectors, particularly the fishing
industry, while women and girls are trafficked for factory and domestic
work; children are trafficked to Vietnam and Thailand for the purpose of
forced begging; Cambodia is a transit and destination point for women from
Vietnam trafficked for sexual exploitation; trafficking for sexual
exploitation also occurs within Cambodia's borders, from rural areas to the
cities
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Cambodia does not fully comply with
the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is
committed to making significant efforts to sustain progress over the coming
year |
|
Illicit drugs:
|


narcotics-related corruption reportedly involving some in the government,
military, and police; limited methamphetamine production; vulnerable to
money laundering due to its cash-based economy and porous borders
|
This page was last
updated on 15 November, 2007 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
